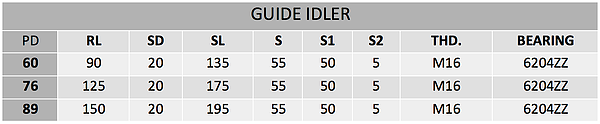
Guide idlers are also called stub idlers, limiting idlers, track-guiding idlers. Guide idlers are are designed to prevent belts from tracking off. usually by contact with the edge of the belt. They can be used on both the trough and return side of the conveyor belt. The problem with many guide idlers is the design itself. A conveyor belt can quickly wear down the steel of the guide roll to make it unusable.
Guide rollers are also called stub rollers, limiting rollers, track-guiding rollers, snub rollers or lateral guide rollers. Guide Idler and Conveyor Belt Tracking Guide, was developed during the 1940's to assure reliable Belt Conveyor Tracking in the following industries: Guide idlers are properly mounted at the sides of the belt so that they keeping it aligned if there are run outs. Continuous belt rubbing against the guide idlers might cause damage (edge wear) of the belt. In that case further check of the conveyor items (pulleys, idlers, etc) and structure should take place. Guide idlers are available in various diameters and lengths.
Guide Idler usually use Ball Bearing.
Guide Idler Guide Idler,Side Guide Idler,Guide Wheel Front Idler Shandong Xinkaite Bearing Co., Ltd. , https://www.idlerbearing.nl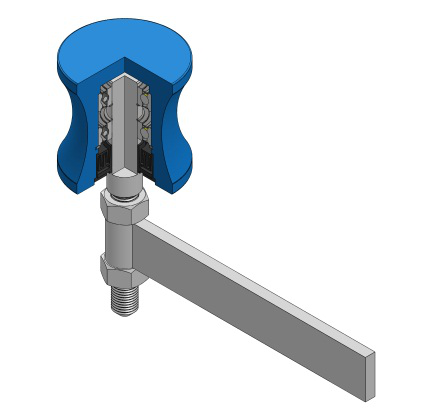

I. Contents of danger and hazard identification
(1) Site: engineering geology, topography, hydrology, meteorological conditions, etc.
(2) The layout of the factory area.
1. General picture: functional partition arrangement, high temperature, hazardous materials, noise, radiation facility layout, process flow arrangement, construction (structure) structure, wind direction, safety distance, health protection, etc.
2. Transportation lines and terminals.
(3) Construction (structure): structure, fire prevention, explosion-proof, orientation, lighting, transportation channels, etc.
(4) Production process: material (toxic, corrosive, flammable) temperature, pressure, speed, operation and control conditions, accidents and out of control.
(5) Production equipment and equipment.
1. Chemical equipment and equipment: high temperature, low temperature, corrosion, high pressure, vibration, spare parts of key parts, control, operation, overhaul and failure, and emergency abnormal conditions;
2. Mechanical equipment: moving parts and workpieces, operating conditions, maintenance work, misoperation and misoperation;
3. Electrical equipment: power failure, electric shock, fire, explosion, smashing operation and misoperation, static electricity, lightning;
4. Equipment with high risk and equipment at high altitude;
5, special monomer equipment, equipment: boiler room, acetylene station, oxygen station, oil depot, dangerous goods library.
(6) Dust, poison, noise, vibration, radiation, high temperature, low temperature and other hazardous parts.
(7) Management facilities, emergency rescue facilities and auxiliary production and living sanitation facilities.
Second, the identification of major hazards
(1) Definition of major accidents: The major accidents defined in the Convention on the Prevention of Major Industrial Accidents adopted by the International Labor Organization (ILO) in 1993 were “suddenly occurring in a production activity within a major hazardous facility, involving one type or Serious accidents, fires, explosions, etc. of various hazardous materials cause accidents caused by acute or chronic serious harm to workers, the public or the environment."
(II) Identification of major hazard sources: Identification according to GB 18218-2000 “Significant Hazard Source Identificationâ€.
Third, the identification and analysis methods of dangerous hazards
(1) The empirical method.
1. Control method: a method for analyzing the hazard and hazard factors of the evaluation object by means of experience and judgment ability against the relevant standards, regulations, checklists or observation and analysis capabilities of the analysts;
2. Analogy method: Use the same or similar engineering system or operating conditions and labor safety and health statistics to analogize and analyze the hazard and hazard factors of the evaluation object.
(II) System safety analysis method: Apply some system safety engineering evaluation methods to identify hazards and hazards. System security analysis methods are often used in new development systems that are complex and have no accident experience. Commonly used system security analysis methods include event trees, accident trees, and so on.